Patel et al.
polysaccharides can act as electron donor to react with
Determination of flocculating activity
free radicals to from stable products (Vamanu et al.,
Qin et al., (2007) suggested that EPS could make
2012).
colloidal and suspended particle in solution which
2. Hydrogen peroxide scavenging assay
justify the EPS is a good flocculating agent and has a
good adsorptive capacity. Particles of charcoal were
The hydrogen peroxide inhibition activity of EPS and
effectively aggregated and precipitated by the addition of
ascorbic acid was increased with increase in incubation
the EPS. With charcoal as the suspended particles, the
time. The scavenging activity of EPS obtained from fungal
FA of the crude supernatant reached, approximately, 99%
isolate SGMP2 was higher than that of the ascorbic acid
flocculating activity without addition of cations such as
and the scavenging activity of EPS obtained from fungal
Ca 2+ and Mg 2+. However, addition of Ca 2+ or Mg 2+ was
isolate SGMP1 was lower than that of the ascorbic acid
found to be necessary to achieve maximum FA of fungal
(Fig.10 (b)). Hydrogen peroxide scavenging activity of
EPS produced by Mucor sp . (Abdel-Aziz et al., 2012).
EPS obtained from marine filamentous fungi Keissleriella
sp. YS 4108 was concentration dependent and maximum
Table 1. EPS production of different isolates
activity 72 % was observed at a concentration of 133 μg/
Culture
EPS (g/l)
Dry cell Biomass (g/l)
ml (Li et al., 2012).
SGMP1
17
7.3
3. ABTS Inhibition assay
SGMP2
15.25
4.1
As shown in Fig.10 (b), the ABTS inhibition activity
SGMP3
4.25
5.4
of EPS and ascorbic acid was increased with increase
SGMP4
3.0
1.0
in concentration of EPS and ascorbic acid. The results
indicate that EPS of fungal origin possessed scavenging
Table 2. Antimicrobial activities of SGMP1 and SGMP2
power for ABTS radicals. Similar type of scavenging
fungal culture against test organism
power was reported in obtained EPS from edible
Test organism
SGMP1(mm)
SGMP2(mm)
mushroom P. ostreatus (Vamanu et al., 2012) and in
Staphylococcus aureus
3
5
thermophilic green alga Cosmarium sp. (Challouf et al.,
Salmonella typhi
9
5
2012).
Escherichia coli
8
7
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
6
8
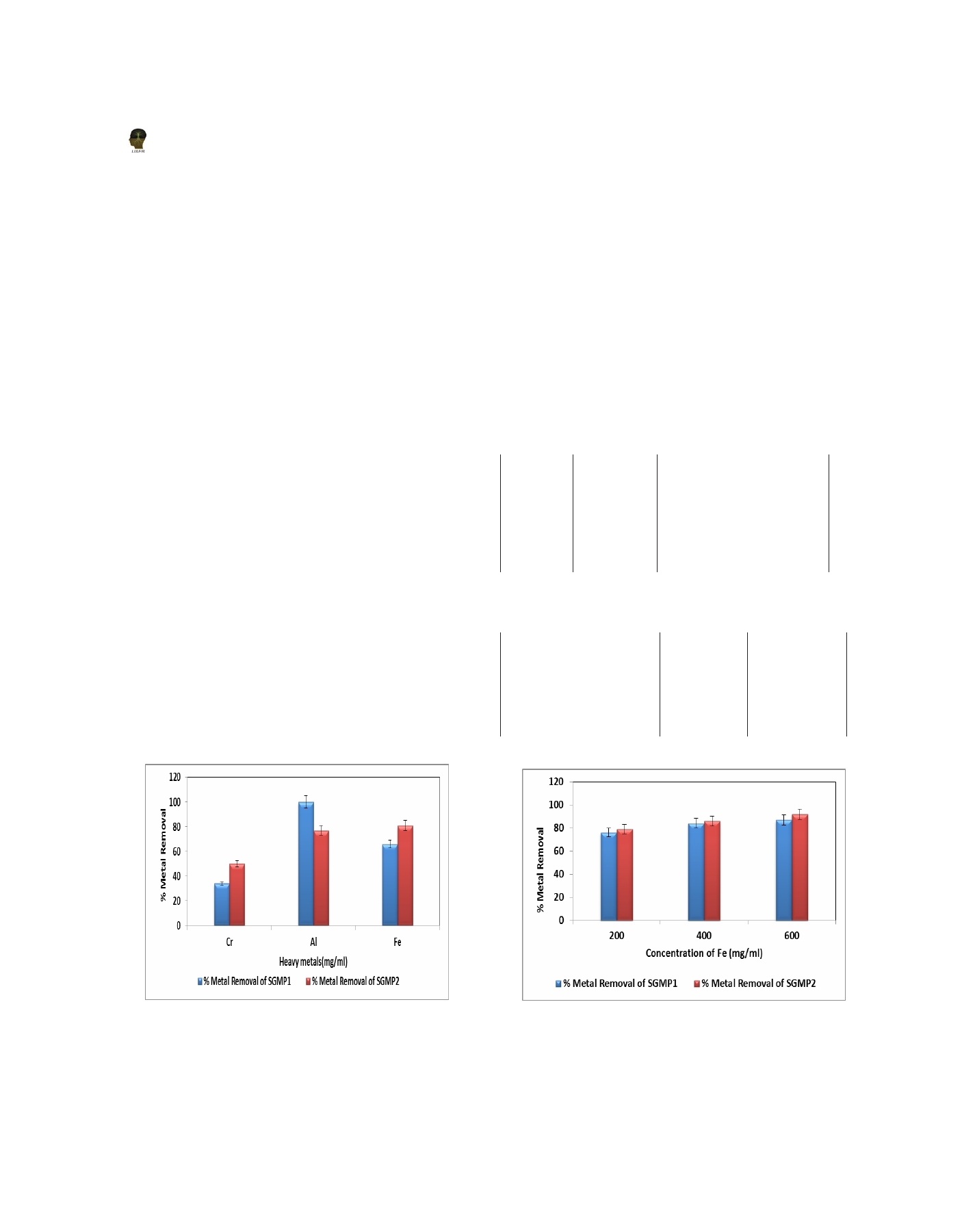
Fig 11(a). various Metal Removal efficiency using fungal
Fig 11(b): Effect of initial Fe +3 on Fe removal efficiency using
isolates SGMP1 and SGMP2
fungal isolates SGMP1 and SGMP2
520