Biopreservative activity of bacteriocin-producing lactic acid bacteria
bacteriocin). The minimum inhibitory concentration
Biopreservative property of bacteriocin in coconut
(MIC) was 50 ul for the bacteriocins of G2 and G3.
water
The MIC was 100 ul for the bacteriocins of G1 and
G4. Vescovo et al., (1995) observed a reduction in
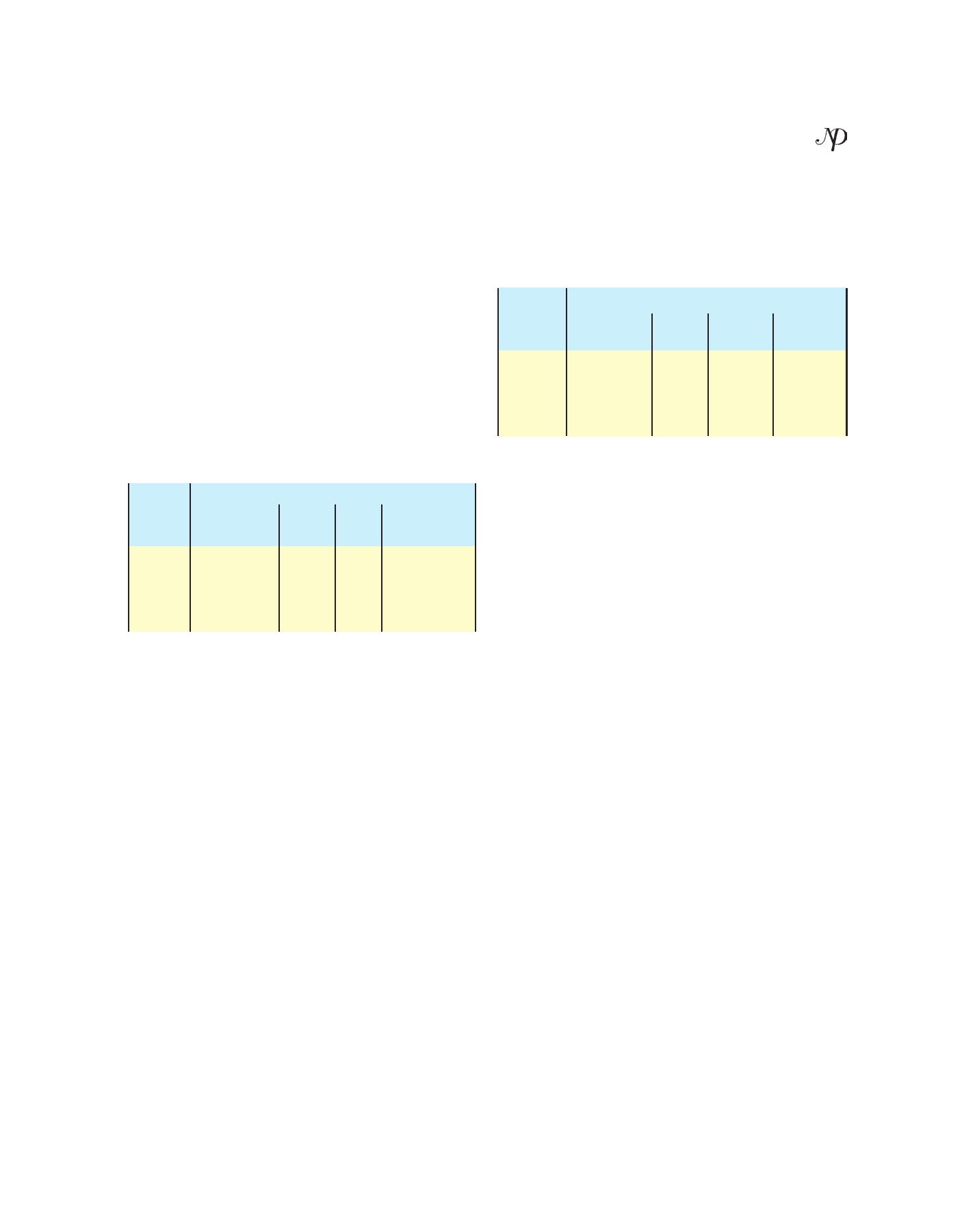
Table 5. After three days (72 hours) - Biopreservative
high initial bacterial loads of ready-to-use mixed
efficacy of bacteriocin in coconut water
salads on addition of bacteriocin producing LAB.
Komitopoulou et al ., (1999) studied the growth of
Bacteriocin concentration in ul
Strain
A. acidoterrestris in fruit juice and its sensitivity to
isolates
In absence of
100 ul
200 ul
400 ul
heat treatment and nisin (Grande et al ., 2005a). In
bacteriocin
our study, the preservative effect of bacteriocins of
G1
+
+
+
-
all the four isolates in apple juice, increased with the
G2
+
+
+
-
increase in the concentration of bacteriocins.
G3
+
+
+
-
G4
+
+
-
-
Table 4. After one day (24 hours) - Biopreservative efficacy
(+): Indicates presence of microbial colonies, (-):- Indicates
of bacteriocin in apple juice
Absence of microbial colonies
Strain
Bacteriocin concentration in ul
At zero time, in the absence (without bacteriocin) or
isolates
In absence of
presence (different concentrations) of bacteriocin in
25 ul
50 ul
100 ul
Bacteriocin
the fresh coconut water didn’t show any bacterial
G1
+
-
-
-
growth and appears to be sterile. At 72 hrs of
G2
+
-
-
-
incubation at room temperature (storage period) with
G3
+
+
-
-
lower concentrations of 25, 50 and 100 microlitres of
G4
+
+
-
-
bactoriocin (Data not shown) the microbial growth
was not inhibited. Therefore, the biopreservative
(+):- Indicates presence of microbial colonies, (-):- Indicates
activity of bacteriocin in coconut water was observed
Absence of microbial colonies
at higher concentrations for 72 hrs. The results (Table
The inhibitory activity of bacteriocins of four isolates
5) suggest, MIC of bacteriocin of G4 was 200 ul, and
(G1, G2, G3 and G4) in apple juice was observed
MIC of G1, G2 and G3 was 400 ul. Applications of
after storage period of one day (24 hours) at room
protective cultures and co-cultures are considered
temperature (Table 4). It was observed that there
as
additional
safety
factors
warranting
the
was absence of microbial colonies with 25 ul of
microbiological stability of the resulting foods
bacteriocin of G1 and G2 isolates. The bacteriocin of
reducing risks of growth and survival of food-borne
G3 and G4 showed complete inhibition with 50 ul.
pathogens and food spoilage organisms (Joshi et
The results revealed that the preservative efficacy al 2006). Esayas et al., (2008) also observed the bio-
of bacteriocin of strains G1 and G2 was higher than
preservative potential of purified bacteriocin from
G3 and G4. Previous studies have demonstrated the
isolate CA44 against B.cereus and found that the
nisin effectiveness in promoting lag phase increase preservative effect in fruit juice increased with the
and growth rate reduction (Chihib et al ., 1999) as well
increase in the concentration of bacteriocin. Eighty
to inactivate contaminants in beer (Galvagno et al. ,
seven per cent reduction of Bacillus cereus population
2007), indicating the potential use of this bacteriocin.
was observed in juice at a concentration of 0.5 %.
The results of table 4 indicate, the MIC of bacteriocins
Hence, the preservative property of bacteriocin of
of G1, G2 was 25 ul. The MIC of bacteriocins of G3
strain G4 was better than bacteriocins of strains G1,
and G4 was 50 ul.
G2 and G3 (Table 5).
125