Molecular characterization of bacterial leaf blight resistant
which occur as interspersed repetitive elements in all
modified CTAB method (Zidani et al ., 2005). All of the
eukaryotic genomes (Tautz and Renz, 1984). Variation in
required reagents were prepared as per Sambrook et al .,
the number of tandemly repeated units is mainly due to
(1989). Fresh leaf tissues (0.3 g) was ground in liquid
strand slippage during DNA replication. Microsatellites
nitrogen and taken into a 2 ml microcentrifuge tube.
are highly popular genetic markers because of their co-
The ground sample was extracted with 0.8 ml of CTAB
dominant inheritance, high abundance, locus-specificity,
extraction buffer. [To prepare 10 ml of CTAB extraction
high reproducibility, multi-allelic nature and the ease
buffer, 1 M Tris HCL (1ml), 0.5 M EDTA (1ml), 5 M NaCl
of assessing SSR size variation by PCR with pairs of
(2.8ml) were mixed with 4 ml of distilled water. Then,
flanking primers.
4% CTAB (0.4g) and 1% PVP (0.1g) were added to this
mixture. Dissolved PVP and CTAB properly and heated
Materials and Methods
this mixture at 60°C (about 20-30 minute). Two percentage
of β-mercaptoethanol (200µl) was added, just before
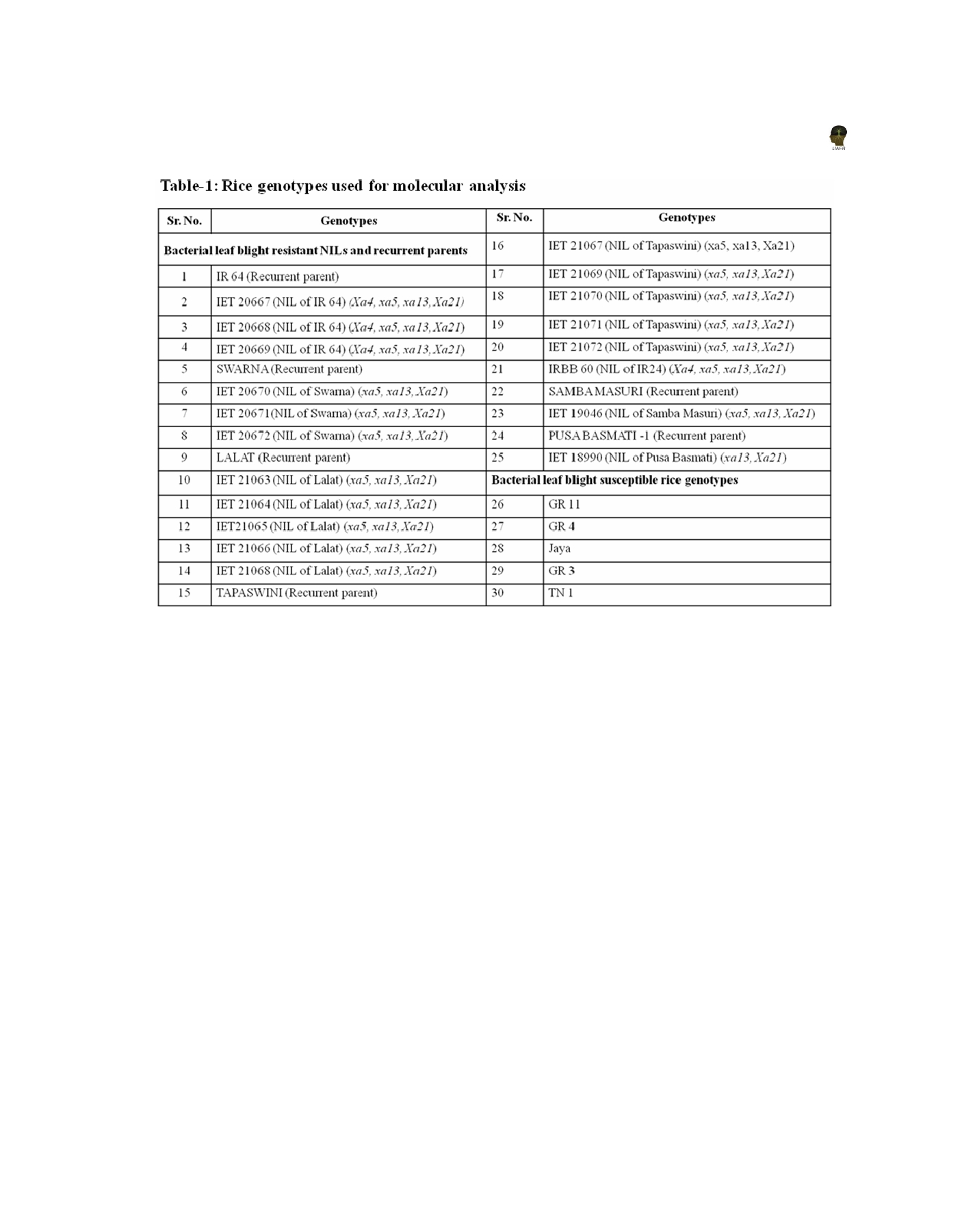
The seeds of 30 rice genotypes (Table 1) which included,
use.] Sample was mixed well with extraction buffer by
19 NILs, six recurrent parents and five susceptible check
inversion. The sample was incubated for one hour at 65°C
cultivars used in the study were obtained from the Main
in water bath (allowed it to cool down). Equal amount of
Rice Research Station, Anand Agricultural University,
800 µl of chloroform: isoamylalcohol (24:1) was added
Nawagam, Gujarat, India.
to centrifuge tube and mixed by inversion. Centrifugation
was carried out it for 20 minutes at 10,000 rpm at 4°C.
Plant material and DNA extraction
Supernatant was transferred into a new tube and further
The seeds of 30 rice genotypes (Table-1) were grown in
extracted with chloroform: isoamyl alcohol (24:1), and
pots, 15 days old seedlings were collected and used for
the DNA was precipitated with 80% ethanol. The pellet
isolating genomic DNA. DNA was extracted using a
was air dried and resuspended in 100µl of Tris–EDTA
429