Growth, yield components and yield of hybrid rice
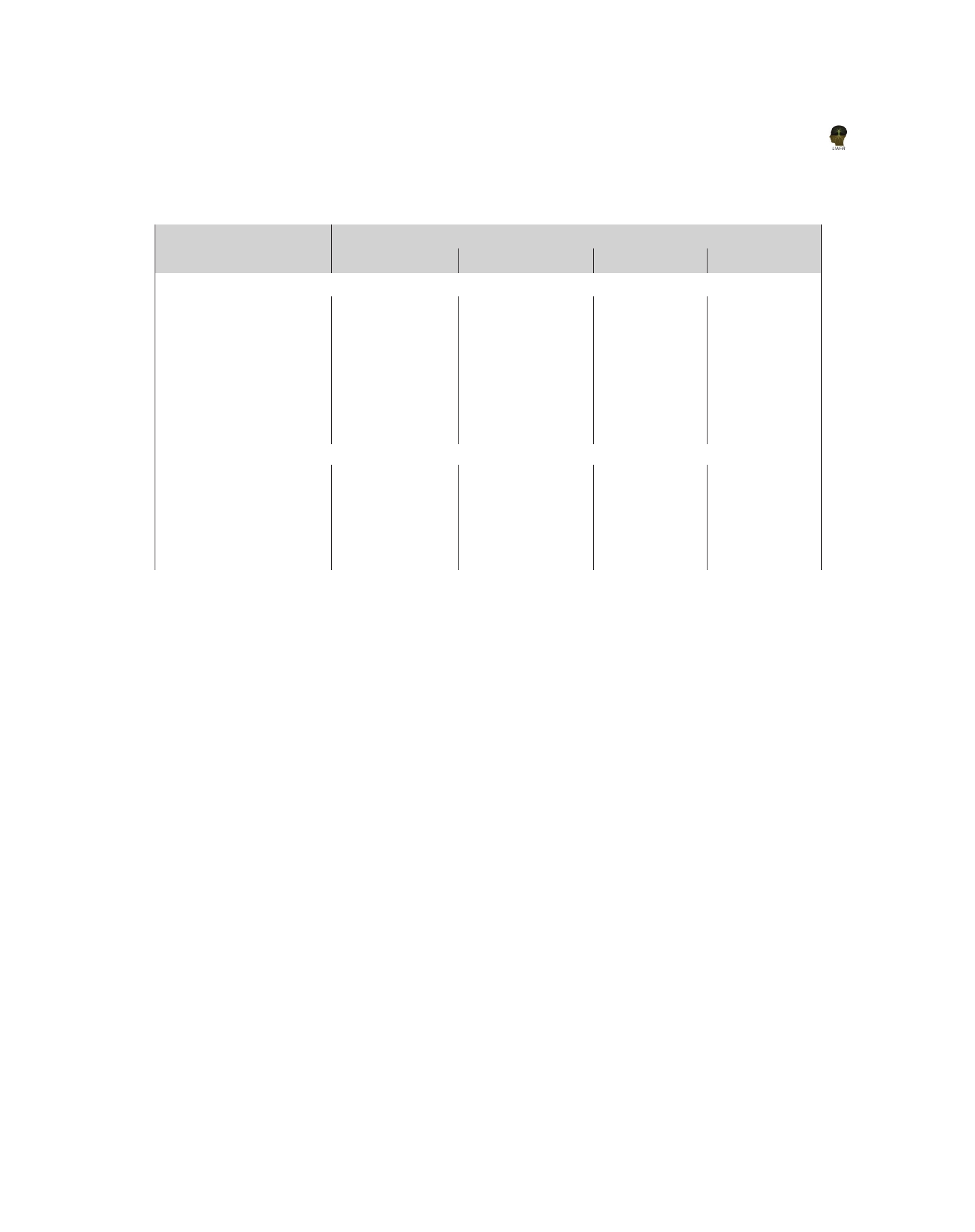
Table 3. Effect of nitrogen level and time of homo-brassinolide application on dry matter accumulation (DMA) at different
stages of hybrid rice
DMA (gm -2 )
Treatments
20 DAT
40DAT
60DAT
80DAT
Nitrogen level (kg/ha)
N0*
109.3
198.9
366.2
497.0
N60
117.9
240.1
508.6
802.1
N120
133.7
267.8
559.7
843.8
N180
145.3
307.8
663.7
948.9
N240
153.6
346.2
757.1
1044.9
SEm(±)
2.5
4.6
5.3
3.9
CD(P=0.05)
7.2
13.3
15.3
11.3
Time of homo-brassinolides application
AT
129.9
255.6
499.0
754.6
AT+PI
131.3
279.5
578.1
833.4
AT+PI+FL
134.8
281.4
636.0
894.0
SEm(±)
1.9
3.6
4.1
3.1
CD(P=0.05)
NS
10.4
11.8
8.9
components like number of panicles m -2 , panicle
The results are in conformity with the findings of
length, number of spikelets and filled grains
Hu et al. , (2007) and Huang et al . (2008). Spraying
panicle -1 , percentage of filled grain and test weight
of homo-brassinolide showed significant effect on
increased steadily up to the application N 180 and
all the yield components of hybrid rice. Spraying of
were comparable to N 240 (Table 4). Both N 180 and N 240
homo-brassinolide at AT+PI+FL and AT+PI recorded
recorded significantly higher number of panicles m -2 ,
significantly higher number of panicles m -2 , longer
longer panicle length, greater number of spikelets
panicle length, greater number of spikelets and filled
and filled grains panicle -1 , higher percentage of filled
grains panicle -1 , higher percentage of filled grain
grain and greater test weight than what obtained at
and greater test weight than what obtained at only
lower nitrogen levels (N 120 , N 60 and N 0 ). The crop at
one application of spraying of homo-brassinolide at
low nitrogen level (N 0 ) produced the lowest values
active tillering stage. The crop at single application
of all the yield components, but was comparable to
of homo-brassinolide produced the lowest values
those obtained at N 120 and N 60 in most of the cases
of all the yield components. Similar type of results
during the study. The tropical rice hybrids are panicle
were reported by Sakamoto et al . (2006) and Bera and
size and require adequate nutrition like nitrogen
Pramanik (2012).
for producing higher number of large size panicles
(Buresh et al. , 2005). Application of lower dose of
Crop productivity
nitrogen (N 60 and N 0 ) did not mitigate the nutrient
The nitrogen level exerted significant effect on grain
need of the crop particularly during its reproductive
yield, straw yield and harvest index (HI) of hybrid
period resulting in lower number of spikelets and
rice. The highest grain yield (6116 kg ha -1 ) was
filled grains panicle -1 with low test weight due
produced in crop receiving N nitrogen level (180
180
to its adverse affect on grain filling of hybrid rice.
kg N ha -1 ); whereas, the highest straw yield (8170kg
821